10:1–13 The Queen of Sheba’s |
10:1 Sheba Possibly located in the southwestern part of the Arabian Peninsula. Sheba was associated with gold and spices (Isa 60:6; Jer 6:20; Ezek 27:22).
was associated with gold and spices (Isa 60:6; Jer 6:20; Ezek 27:22).
hard questions The Hebrew word used here, chidah, can describe a riddle (Judg 14:12–20) or a teaching from elders (Prov 1:6; Psa 78:2).
10:2 very great wealth The Hebrew word used here, chayil, often refers to force in a military sense (see 2 Kgs 6:15; 18:17) but it also can be related to wealth (Isa 60:5–6).
spices The word bosem is a generic term for aromatic spices.
her heart The Hebrew term used here, levav, comes from the Hebrew word lev, which means “inner person,” “mind,” “will,” or “heart.”
10:4 the wisdom of Solomon Solomon’s wisdom includes knowledge of nature (1 Kings 4:33) and the ability to speak proverbs, compose songs (4:32), reorganize a nation (4:1–28), and judge difficult cases (3:16–28). Here, the author associates Solomon’s wisdom with his wealth (see 3:13).
10:5 cupbearers Perhaps refers to waiters (2 Chr 9:4).
burnt offerings which he offered Solomon offered burnt sacrifices three times per year (1 Kgs 9:25). On burnt offerings, see note on Lev 1:3.
three times per year (1 Kgs 9:25). On burnt offerings, see note on Lev 1:3.
10:7 Your wisdom and prosperity surpass God granted Solomon wealth as a reward for requesting wisdom (1 Kings 3:13; see note on v. 4; compare Prov 3:16).
10:9 has delighted in you Hiram, King of Tyre, similarly praises Solomon (1 Kings 5:7).
similarly praises Solomon (1 Kings 5:7).
10:10 a hundred and twenty talents of gold Likely a tribute payment (see 4:21 and note). Hiram presents Solomon with the same amount (9:14).
10:11 the fleet of ships of Hiram See note on 5:1.
almug wood This is the only occurrence in the ot of the Hebrew word used here, almuggim. The exact identification of this species of wood is uncertain, but it is to be understood as a luxury item.
10:12 a raised structure The Hebrew term mis'ad—which occurs only here in the ot—comes from the word sa'ad, meaning “to support.” The exact meaning of this architectural term is uncertain.
the house of Yahweh Described in chs. 6–7.
singers Singers provided entertainment in the royal court (2 Sam 19:35; 2 Chr 35:25) and also took part in ritual services (Ezek 40:44).
provided entertainment in the royal court (2 Sam 19:35; 2 Chr 35:25) and also took part in ritual services (Ezek 40:44).
10:13 all of her desire that she asked May indicate that this was a diplomatic mission and the two negotiated an agreement.
King Solomon freely offered her The Hebrew phrase used here, keyad hammelekh shelomoh, refers to the king’s generosity (see also Esth 1:7; 2:18). Solomon apparently gave the Queen of Sheba gifts in return (compare 1 Kgs 10:2).
10:14–29 This catalog of Solomon’s possessions may be read as either evidence of a “golden age” brought about by Solomon’s wisdom or a critique of amassing wealth. This passage appears between the Queen of Sheba’s visit with Solomon, whose wisdom leaves her overwhelmed (v. 5), and the account of Solomon’s foreign wives, who lead him astray (11:9). |
10:14 in one year The Hebrew terminology here is vague; it might be referring to the gold that Solomon received in one certain year, rather than an annual amount.
six hundred and sixty-six talents of Perhaps an approximate summary of the stated amount of gold from Hiram (120 talents; 9:14), Ophir (420 talents; 9:28), and Sheba (120 talents; v. 10). A talent was about 75 pounds (34 kilograms). These 666 talents are equal to almost 50,000 pounds (22,600 kilograms).
10:15 the governors of the land Administrators from the 12 provinces of Israel were responsible for providing a month’s worth of royal provisions (4:1–28).
10:16 two hundred shields of hammered gold The Hebrew word used here, tsinnah, describes a body-length shield,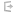 possibly with three sides (Psa 5:12). An attendant carried this same type of shield for Goliath (1 Sam 17:7). Despite their size, gold is a relatively soft metal and thus these shields would not hold up in battle.
possibly with three sides (Psa 5:12). An attendant carried this same type of shield for Goliath (1 Sam 17:7). Despite their size, gold is a relatively soft metal and thus these shields would not hold up in battle.
six hundred measures of gold A shekel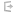 is about 0.4 ounces (11 grams). Each shield weighed 15 pounds (6.6 kilograms).
is about 0.4 ounces (11 grams). Each shield weighed 15 pounds (6.6 kilograms).
10:17 three hundred small shields of The Hebrew word used here, magen, refers to small, hand-held shields.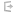
three minas of A mina is about 1.25 pounds (0.6 kilograms). Each shield weighed 3.75 pounds (1.8 kilograms).
into the House of the Forest of Lebanon See note on 1 Kings 7:2.
10:18 a large ivory throne Likely a wood throne with ivory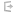 inlays. Costly furniture in the ancient Near East often had carved ivory plates inlaid in the woodwork. The prophet Amos critiques the wealthy and conceited for lying on beds of ivory (Amos 6:4).
inlays. Costly furniture in the ancient Near East often had carved ivory plates inlaid in the woodwork. The prophet Amos critiques the wealthy and conceited for lying on beds of ivory (Amos 6:4).
10:19 a circular top The traditional Hebrew text refers to the round top of the throne; round-topped chairs and bovine imagery were common throughout the ancient Near East. However, the ancient Greek translation, the Septuagint, suggests the top of the throne had a carving of a calf or bull’s head. It may be that the Greek text is more original, since the calf imagery would have been seen as related to idolatry and thus the Hebrew text may have later been altered (Exod 32; compare 1 Kgs 12:25–33).
two lions Symbols of strength and power throughout the ancient Near East (Ezek 19:1–9; Nah 2:12–13). In the ot, lion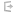 imagery is associated with Judah, King David’s tribe (Gen 49:9).
imagery is associated with Judah, King David’s tribe (Gen 49:9).
beside the armrests Animal figures were often worked into armrests, but here they are described as beside the throne.
10:20 nothing like this was made It is unclear in what way Solomon’s throne was unique, since archeological discoveries reveal similar thrones.
10:21 the House of the Forest of Lebanon See note on 1 Kgs 7:2.
three years Indicates a very long journey, not necessarily the exact length of the voyage.
10:23 with respect to wealth and wisdom Concerning amassing riches, see Deut 17:17 and note. See note on 1 Kings 10:4.
10:24 All of the earth was seeking the presence of Solomon A repeated motif throughout the account of Solomon’s reign (3:9, 12, 28; 4:34; 10:1–13).
which God had put in his heart See 3:11–12.
his heart From the Hebrew word lev. The word lev means “inner-person,” “mind,” “will,” or “heart.” People in the ancient Near East associated the heart with comprehension, not emotion.
10:25 his gift The Hebrew word used here, minchah, describes a required payment brought from a lesser power to its governing power (2 Kgs 17:3; Judg 3:15, 17; 2 Sam 8:2, 6).
10:26 twelve thousand horses Coincides with the 12,000 horses listed in 4:26.
the cities of the chariots Perhaps includes some of the cities listed in 9:15–18. The large stables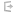 at Megiddo suggest that it may have served as one of Solomon’s cavalry cities.
at Megiddo suggest that it may have served as one of Solomon’s cavalry cities.
10:27 cedars See 5:6 and note; 5:8 and note.
the sycamore fig trees The Hebrew word used here, shiqmahi, refers to the ficus sycomorus, a tree which was common in the low hills of Israel and suitable for roofing.
Shephelah Refers to the low hills in Judah between the coastal plain and Jerusalem.
10:28 Kue A kingdom in southeast Asia Minor (modern-day Turkey).
10:29 A chariot went up and went out The Hebrew phrase used here, literally “would go up and out,” implies that chariots were purchased with the intent to resell. Solomon amasses wealth through both trade and tribute.
six hundred silver A shekel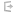 is about 0.4 ounces (11 grams). A chariot cost about 15 pounds (6.6 kilograms) of silver.
is about 0.4 ounces (11 grams). A chariot cost about 15 pounds (6.6 kilograms) of silver.
the Hittites See Gen 10:15 and note.
The Hittite empire, based in Asia Minor (modern-day Turkey), was a major power in the ancient Near East during the 17th–12th centuries bc (prior to Israel’s monarchy). Groups of Hittites migrated south, eventually settling in the hill country of Canaan near Hebron (Gen 23:19–20; Num 13:29). Notable Hittites in the Bible include Ephron, from whom Abraham purchased a burial site (Gen 23) and Uriah, one of David’s mighty men (2 Sam 23:39). Esau married two Hittites (Gen 26:34), and Solomon had Hittite women in his harem (1 Kgs 11:1). |

|
About Faithlife Study BibleFaithlife Study Bible (FSB) is your guide to the ancient world of the Old and New Testaments, with study notes and articles that draw from a wide range of academic research. FSB helps you learn how to think about interpretation methods and issues so that you can gain a deeper understanding of the text. |
| Copyright |
Copyright 2012 Logos Bible Software. |
| Support Info | fsb |
 Loading…
Loading…

 Hittites
Hittites